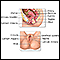
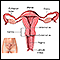
Retroversion of the uterus
Definition
Retroversion of the uterus occurs when a woman's uterus (womb) tilts backward rather than forward. It is commonly called a "tipped uterus."
Alternative Names
Uterus retroversion; Malposition of the uterus; Tipped uterus; Tilted uterus
Causes
Retroversion of the uterus is common. Approximately 1 in 5 women has this condition. The problem may also occur due to weakening of the pelvic ligaments at the time of menopause.
Scar tissue or adhesions in the pelvis can also hold the uterus in a retroverted position. Scarring may come from:
- Endometriosis
- Infection in uterus or tubes
- Pelvic surgery
Symptoms
Retroversion of the uterus almost never causes any symptoms.
Rarely, it may cause pain or discomfort.
Exams and Tests
A pelvic exam will show the position of the uterus. However, a tipped uterus can sometimes be mistaken for a pelvic mass or a growing fibroid. A rectovaginal exam may be used to distinguish between a mass and a retroverted uterus.
An ultrasound exam can accurately determine the exact position of the uterus.
Treatment
Treatment is not needed most of the time. Underlying disorders, such as endometriosis or adhesions, should be treated as needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
In most cases, the condition does not cause problems.
Possible Complications
In most cases, a retroverted uterus is a normal finding. However, in some cases it may be caused by endometriosis, salpingitis, or pressure from a growing tumor.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have ongoing pelvic pain or discomfort.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent the problem. Early treatment of uterine infections or endometriosis may reduce the chances of a change in the position of the uterus.
References
Advincula A, Truong M, Lobo RA. Endometriosis: etiology, pathology, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 19.
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Female genitalia. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 19.
Hertzberg BS, Middleton WD. Pelvis and uterus. In: Hertzberg BS, Middleton WD, eds. Ultrasound: The Requisites. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 23.
Review Date:4/19/2022
Reviewed By:John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.